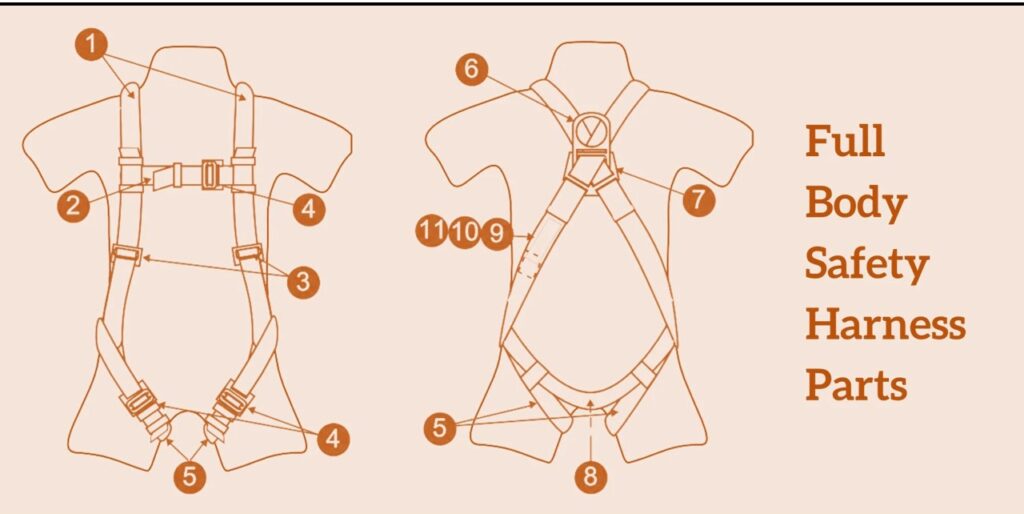
A full body safety harness is vital personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to protect workers from falls in industries like construction, maintenance, and telecommunications. Understanding each harness component is essential for maximizing safety and functionality. This guide highlights the key components of a full body harness, detailing their roles, features, and best practices for use and maintenance.
1.-Shoulder Straps in Full Body Harness: Key Features & Best Practices
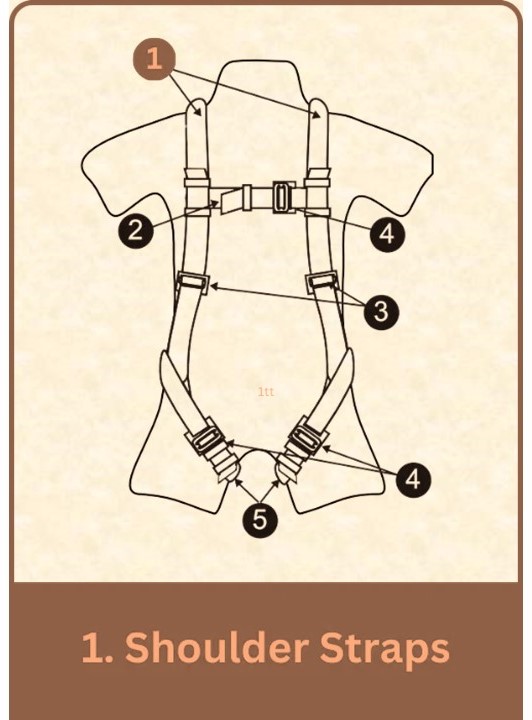
Features:
- Adjustability: Easily adjustable to fit various body sizes, ensuring a secure and snug fit.
- Padding: Provides extra comfort, especially for prolonged use.
- Alignment: Ensures proper positioning on the back for balance and reduced fatigue.
Best Practices:
- Regular Adjustment: Continuously adjust during work to maintain safety.
- Inspection: Check for wear, fraying, or damage regularly.
2. Chest Strap
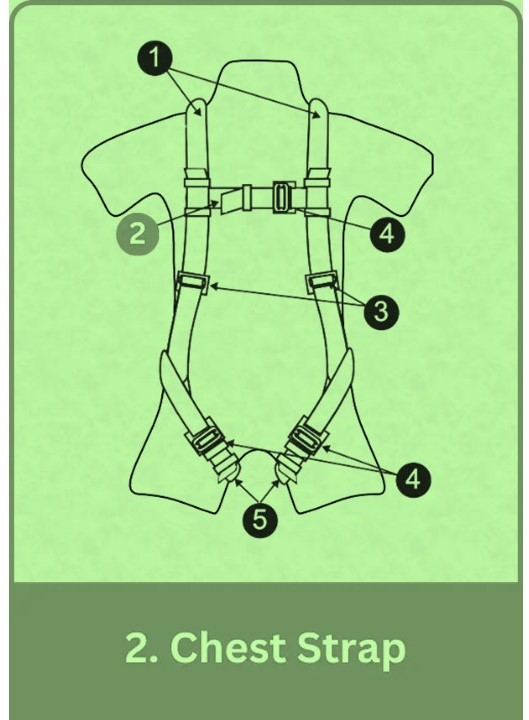
Chest Strap in Full Body Harness: Key Role & Best Practices
The chest strap prevents the harness from riding up over the shoulders during a fall, keeping the harness in the proper position to absorb fall forces.
Placement:
- Position: Mid-chest, 6 to 8 inches below the trachea.
- Height: Avoid placing it too high (risk of strangulation) or too low (harness shift).
Adjustment:
- Tightness: Keep shoulder straps taut but allow free movement.
- Securing: Fasten securely without excess slack.
Best Practices:
- Maintain position and inspect regularly for damage or misalignment.
3. Torso Adjustment

Torso Adjustment Mechanism in Full Body Harness: Key Features & Importance
The torso adjustment mechanism ensures a snug, secure fit for various body sizes, enhancing fall protection.
Features:
- Adjustable Buckles: Allow easy tightening or loosening for a customized fit.
- Multiple Adjustment Points: Located on shoulder, chest, and leg straps for full customization.
Importance: A properly adjusted harness ensures even force distribution and prevents movement during a fall.
Best Practices:
- Personal Fit: Adjust before each use for comfort and safety.
- Avoid Over-Tightening: Ensure a snug but comfortable fit.
4. Parachute/Tongue Buckle/Quick-Connect Fastener
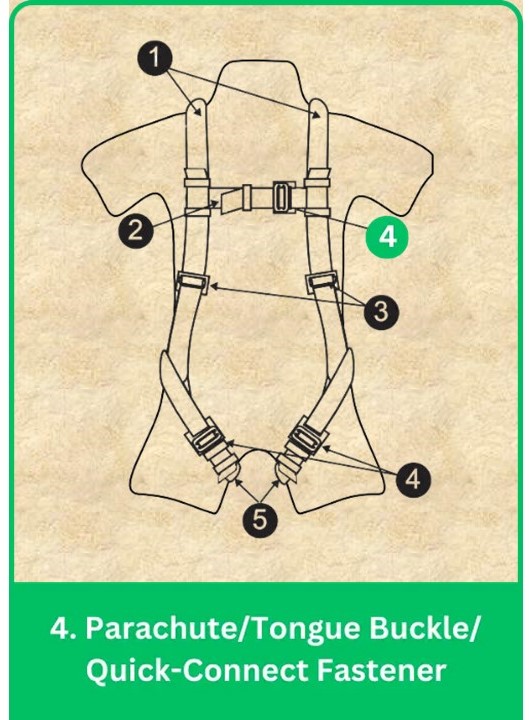
Harness Buckles: Types, Features & Best Practices
Harness buckles ensure the straps stay secure, providing fast donning and doffing while maintaining safety.
Types:
- Parachute-Style Buckles: Provide secure, reliable connections.
- Tongue Buckles: Lock securely using a protruding tongue.
- Quick-Connect Fasteners: Offer rapid attachment and detachment for convenience.
Features:
- Durability: Built from high-strength materials to withstand forces.
- Ease of Use: Simple operation, even with gloves.
- Self-Locking Mechanism: Prevents accidental release.
Best Practices:
- Ensure all buckles are fully engaged before work.
- Regularly inspect for wear or damage.
5. Thigh Straps
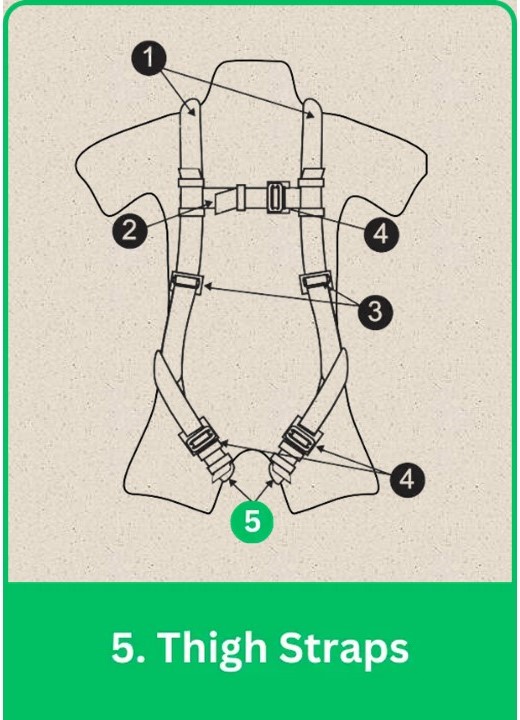
Thigh Straps in Full Body Harness: Key Role & Best Practices
Thigh straps secure the lower body, preventing harness slippage and ensuring effective force distribution during a fall.
Adjustment:
- Snug Fit: Tight enough to prevent movement without restricting circulation.
- Positioning: Properly placed between the thighs for stable support.
Best Practices:
- Comfort and Security: Adjust for a secure fit without excessive slack, allowing full mobility.
- Regular Checks: Inspect for wear or damage before each use.
6. Dorsal D-Ring

Dorsal D-Ring in Full Body Harness: Key Role & Best Practices
The dorsal D-ring is the primary attachment point for lanyards in fall arrest systems, ensuring safe fall protection.
Placement:
- Location: Positioned between the shoulder blades for optimal force distribution.
- Accessibility: Easily reachable for quick lanyard attachment.
Usage:
- Compatibility: Use with compatible connectors to prevent disengagement.
- Single Point: Typically used as the only attachment for fall arrest.
Best Practices:
- Secure Attachment: Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper lanyard connection.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the D-ring’s load capacity.
7. Back Plate

Back Plate in Full Body Harness: Role & Best Practices
The back plate enhances support and distributes fall forces across the back and shoulders, improving stability and comfort.
Importance:
- Reinforced Construction: Built from durable materials to withstand dynamic loads during a fall.
- Comfort Padding: Often includes padding for prolonged comfort.
Best Practices:
- Proper Fit: Ensure the back plate is correctly positioned to prevent shifting.
- Inspection: Regularly check for wear, deformation, or damage.
8. Sub-Pelvic Strap
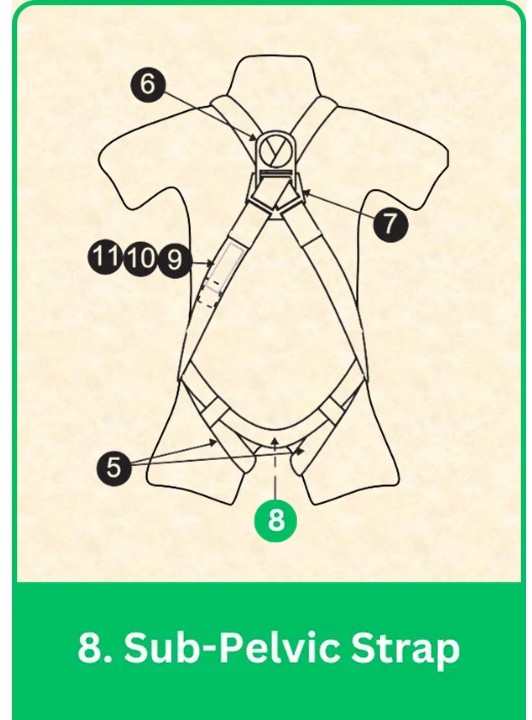
Sub-Pelvic Strap in Full Body Harness: Key Role & Best Practices
The sub-pelvic strap supports the lower back and pelvis, transferring fall forces away from vital organs and providing a secure seat for stability and comfort.
Placement:
- Location: Positioned around the lower abdomen for effective weight support in a seated position.
- Alignment: Ensures even distribution of fall forces across the pelvis and lower back.
Best Practices:
- Adjust for Comfort: Fit snugly without restricting movement.
- Ensure Stability: Check that the strap remains secure and does not shift during use.
9. Inspection/ID Label
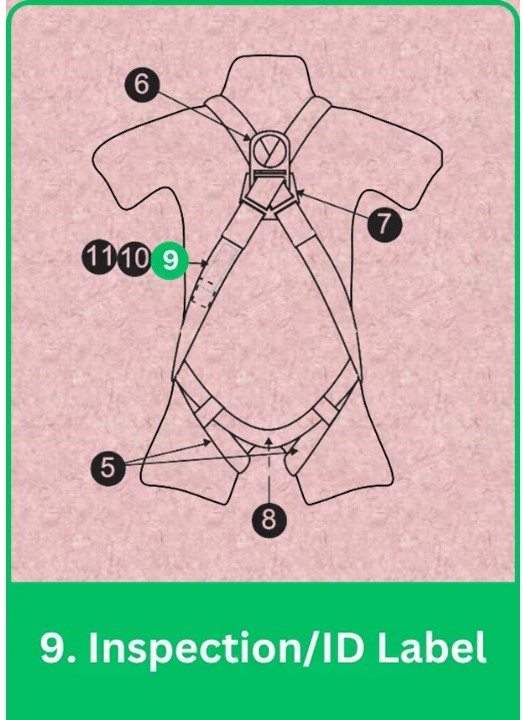
Inspection/ID Label in Full Body Harness: Importance & Best Practices
The inspection/ID label provides essential information, including model number, serial number, purchase date, first use date, and inspection dates, ensuring harness traceability and compliance.
Importance:
- Usage Record: Maintains a history of usage and inspections for safety compliance.
Features:
- Durable Printing: Printed with materials resistant to wear and environmental damage.
- Clear Layout: Organized for easy reading and updates.
Best Practices:
- Accurate Recording: Fill out all fields accurately during inspections.
- Regular Updates: Update the label after each inspection or maintenance.
10. Warning/Instruction Label
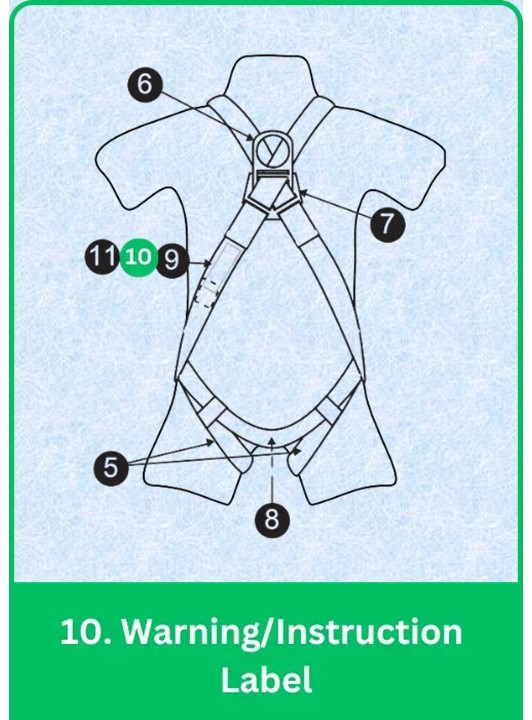
Safety Labels in Full Body Harness: Importance & Best Practices
Safety labels provide critical warnings and instructions for proper harness use, serving as immediate reminders for users.
Placement:
- Visibility: Positioned for easy visibility, typically near the chest or back D-ring.
Content:
- Safety Warnings: Indicate potential hazards and misuse practices.
- Operational Instructions: Guide on how to don, adjust, and use the harness correctly.
Best Practices:
- Read Before Use: Always review warnings and instructions prior to use.
- Regular Reference: Periodically refer to labels to reinforce safety practices.
11. Standards Label

Full Body Safety Harness: Essential Components & Best Practices
A full body safety harness is vital for personal fall protection, designed to safeguard workers in high-risk industries. Understanding key components like connectors and attachment points ensures safety and effectiveness during fall arrest.
Compliance and Importance
The compliance label indicates adherence to safety standards (ANSI, OSHA, CSA), ensuring the harness has been tested for reliability.
Connectors and Attachment Points
Connectors link the harness to fall protection systems, effectively distributing fall forces.
1. Self-Locking Snap Hooks
- Features: Automatic locking, high strength (5,000 lbs), ease of use.
- Best Practices: Verify closure, inspect regularly, store properly.
2. Karabiners
- Types: Locking (for safety) and non-locking (for rotation).
- Best Practices: Use locking for fall arrest, avoid overloading, ensure proper orientation.

3. Quick-Connect Fasteners
- Features: One-handed operation, self-locking, durable.
- Best Practices: Confirm engagement, inspect for wear, ensure compatibility.
Conclusion
Adhering to best practices—adjustment, inspection, and maintenance—enhances harness reliability and workplace safety. Continuous training and diligent upkeep minimize fall risks, fostering a secure working environment.
#StaySafeWithAviraz #SafeAndSecureWithAVIRAZ #SafetyFirstWithAVIRAZ #SafeAndSecureWithAVIRAZ #SafetyFirstWithAVIRAZ
